UID2 Client-Server Integration Guide for Mobile
This guide is for mobile app publishers who want to integrate with UID2 by generating UID2 tokens server-side via a Public Operator or Private Operator and then passing the tokens and user identities into their mobile apps, which will in turn pass the tokens for bidstream use.
This is called client-server integration because some integration steps are client-side and some are server-side.
If you want to integrate with UID2 via client-side only changes (that is, all integration changes required are within the mobile apps), refer to the UID2 Client-Side Integration Guide for Mobile instead.
This page provides a high-level overview of integration steps and links to additional documentation.
UID2 provides mobile SDKs for Android and iOS. Each SDK has the following features:
- Takes in a UID2 identity (a UID2 token and associated values) and persists it in local file storage.
- Automatically refreshes UID2 tokens.
This guide uses the group term UID2 mobile SDKs to include both the SDK for Android and the SDK for iOS.
For FAQs relating to mobile publisher integrations, see FAQs for Mobile Integrations.
You'll need to complete the following steps:
- Complete UID2 account setup and configure account.
- Implement server-side token generation.
- Add the UID2 mobile SDK to your mobile app.
- Configure the UID2 mobile SDK.
- Check that the token was successfully generated and then pass it for bidstream use.
- Optionally, integrate the UID2 GMA/IMA Plugin for GAM Secure Signals integration.
Mobile SDK Version
This guide provides instructions for using either of these UID2 mobile SDKs:
- SDK for Android (version 1.6.0 or later)
- SDK for iOS (version 1.7.0 or later)
For instructions for installing the correct SDK/version into your mobile app, see Add the UID2 Mobile SDK to Your Mobile App.
Integrating with Single Sign-On (SSO)
If you integrate with one or more SSO providers to offer SSO login, you might be able to retrieve the logged-in user's email address from the SSO provider to generate UID2 tokens.
For details, see Publisher Integration with SSO Providers.
Preparing DII for Processing
It's critical that the input data, which you are converting to UID2, is in an acceptable format. If it isn't, you won't get the expected results. For example, you must normalize phone numbers to include the country code, as explained in Phone Number Normalization.
For details, see Preparing Emails and Phone Numbers for Processing.
Complete UID2 Account Setup and Configure Account
To integrate with UID2, you'll need to have a UID2 account. If you haven't yet created an account, first follow the steps described on the Account Setup page.
When initial account setup is complete, you'll receive instructions and a link to access the UID2 Portal, where you can create your credentials for the production environment and configure additional values, if needed. For details, see Getting Started with the UID2 Portal.
For a client-server integration you'll need to set up these values, in the UID2 Portal on the API Keys page:
- API key, also called a client key
- Client secret, a value known only to the participant and the UID2 service
It's very important that you keep these values secure. For details, see Security of API Key and Client Secret.
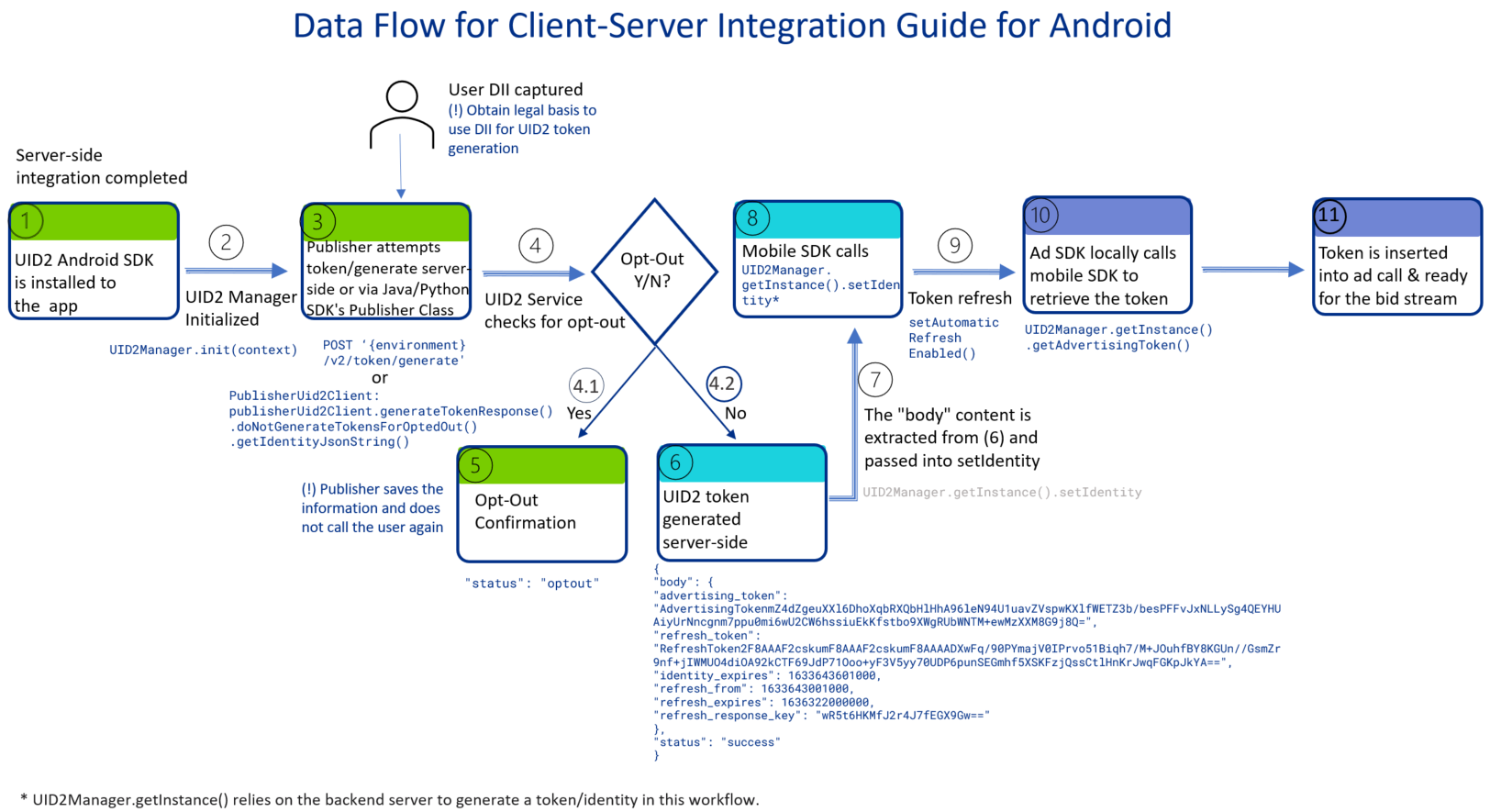
Client-Server Mobile Integration Data Flow Overview
The following diagram shows the data flow that the publisher must implement for UID2 client-server mobile integration.
This example uses the SDK for Android in the client-side mobile app and the SDK for Java on the server side.
Implement Server-Side Token Generation
For a client-server UID2 integration for mobile, the first step is to be able to generate the UID2 token on your server. Then, you can pass the token into your mobile apps for sending to the RTB bidstream.
For details, including instructions and examples, see Server-Side Token Generation.
You will need to pass the Identity response into the mobile app: see Configure the UID2 Mobile SDK.
For security reasons, the API key and secret used in token generation must be called server-side. Do not store these values inside a mobile app.
Server-Side Token Refresh
Token refresh is automatically enabled inside the UID2 mobile SDKs; you don't need to manage it explicitly on the server side.
You might decide to do server-side token refresh if you want to keep your changes in the mobile apps as simple as possible.
If you want to manage token refresh on the server side and not the client/mobile side, you can do so using one of the following:
-
Call the POST /token/refresh endpoint.
-
Use one of the Publisher Client classes, in one of the UID2 server-side SDKs. These classes simplify the request into a single method call.
For instructions, see SDK for Java, Usage for Publishers, Basic Usage Server-Side Integration section or SDK for Python, Usage for Publishers, Server-Side Integration section.
Then, pass the newly refreshed Identity value to the mobile app by following the rest of this guide.
Add the UID2 Mobile SDK to Your Mobile App
For installation instructions, refer to one of the following:
At this point, you are ready to use the UID2 Identity generated server-side in the mobile SDK.
Using the UID2 Integration Environment
By default, the SDK is configured to work with the UID2 production environment: https://prod.uidapi.com. If you want to use the UID2 integration environment instead (for credentials, see Getting Your Credentials), provide the following URL in your call to UID2Manager initialization.
For information about getting credentials for each environment, see Getting Your Credentials.
- Android
- iOS
UID2Manager.init(
context = this,
UID2Manager.Environment.Custom("https://operator-integ.uidapi.com")
)
// Must be set before UID2Manager.shared is accessed
UID2Settings.shared.uid2Environment = .custom(
url: URL(string: "https://operator-integ.uidapi.com")!
)
Bear in mind the following differences between environments:
- Tokens from the UID2 integration environment are not valid for passing to the bidstream.
- You'll have a different set of API key and client secret values for each environment (integration and production). Be sure to use the correct values for each environment.
Optional: Specifying the API Base URL to Reduce Latency
By default, this SDK makes calls to a UID2 production environment server in the USA.
For information about how to choose the best URL for your use case, and a full list of valid base URLs, see Environments.
To specify a UID2 server that is not the default, you can change it in the init call:
- Android
- iOS
UID2Manager.init(
context = this,
UID2Manager.Environment.Signapore
)
// or
UID2Manager.init(
context = this,
UID2Manager.Environment.Custom("https://global.prod.uidapi.com")
)
UID2Settings.shared.uid2Environment = .singapore
// or
UID2Settings.shared.uid2Environment = .custom(
url: URL(string: "https://global.prod.uidapi.com")!
)
Configure the UID2 Mobile SDK
After you've instantiated UID2Manager correctly in your mobile app, you'll need to pass a UID2 identity generated server-side (see Implement server-side token generation), and then pass it into the mobile app using the setIdentity method, as shown in the following:
- Android
- iOS
UID2Manager.getInstance().setIdentity()
UID2Manager.shared.setIdentity()
Token Storage
After you call the setIdentity method, the UID2 identity is persisted in local file storage.
The format of the file stored in the local file storage, or the filename itself, could change without notice. We recommend that you do not read or update the file directly.
Pass Generated Token for Bidstream Use
To retrieve the token, in your mobile app, call the following:
- Android
- iOS
UID2Manager.getInstance().getAdvertisingToken()
UID2Manager.shared.getAdvertisingToken()
If a successful identity was added into the UID2Manager, this method returns a string such as the following:
A4AAAABlh75XmviGJi-hkLGs96duivRhMd3a3pe7yTIwbAHudfB9wFTj2FtJTdMW5TXXd1KAb-Z3ekQ_KImZ5Mi7xP75jRNeD6Mt6opWwXCCpQxYejP0R6WnCGnWawx9rLu59LsHv6YEA_ARNIUUl9koobfA9pLmnxE3dRedDgCKm4xHXYk01Fr8rOts6iJj2AhYISR3XkyBpqzT-vqBjsHH0g
You can use this identity to pass downstream for sending in the RTB bidstream.
If the getAdvertisingToken() method call returns null, there was no identity or valid token generated. Some possible reasons for this, and some things you could do to troubleshoot, are as follows:
- The identity is invalid. In this scenario there are a couple of options:
- Check to see whether there are any errors from the previous
setIdentity()call. - Check the status of the identity, using one of the following:
- Android Java:
UID2Manager.getInstance().getCurrentIdentityStatus() - Android Kotlin:
UID2Manager.getInstance().currentIdentityStatus() - iOS:
UID2Manager.shared.identityStatus
- Android Java:
- Check to see whether there are any errors from the previous
- You could enable logging (set
isLoggingEnabledtotrue) to get more information: see Enable Logging. - The advertising token inside the UID2 identity has expired, and the refresh token has also expired, so the SDK cannot refresh the token.
If there is no identity, follow the instructions in Implement Server-Side Token Generation again, generate a new identity, and pass the result into your mobile app's UID2Manager again.
When to Pass a new UID2 Identity/Token into the SDK
The best way to determine whether a new UID2 identity is required by the UID2 SDK again is to call the getAdvertisingToken() method in all cases:
- Android
- iOS
UID2Manager.getInstance().getAdvertisingToken()
UID2Manager.shared.getAdvertisingToken()
On startup/resumption of the app, if getAdvertisingToken() returns null, it is time to generate new identity on the server by following the instructions in Implement Server-Side Token Generation. Then, pass the result into the mobile app’s UID2Manager again: see Configure the UID2 Mobile SDK.
Enable Logging
The UID2 SDK can generate logs, which could help in debugging any issues during UID2 integration work. To enable logging, do the following:
- Android
- iOS
// During UID2Manager initialization:
UID2Manager.init(
context = this,
isLoggingEnabled = true
)
// On iOS, you must set UID2Settings before you first access UID2Manager.shared.
// Changes made to settings after first access are not read.
UID2Settings.shared.isLoggingEnabled = true
Enable Automatic Token Refresh in Mobile App/Client Side
By default, after a valid UID2 identity has been passed into the UID2Manager, it performs automatic token refresh. If for any reason token refresh was disabled, you can enable it with the following method call:
- Android
- iOS
Android Java:
UID2Manager.getInstance().setAutomaticRefreshEnabled(false)
Android Kotlin:
UID2Manager.getInstance().automaticRefreshEnabled = false
UID2Manager.shared.automaticRefreshEnabled = false
Optional: UID2 GMA/IMA Plugin for GAM Secure Signals integration
If you intend to generate UID2 tokens to send to the Google GMA SDK or the Google IMA SDK, assuming you have followed the instructions in this guide, you must also add the UID2 GMA/IMA plugins into your mobile app. For instructions, refer to the applicable plug-in guide:
- UID2 GMA Plugin for Android Integration Guide
- UID2 GMA Plugin for iOS Integration Guide
- UID2 IMA Plugin for Android Integration Guide
- UID2 IMA Plugin for iOS Integration Guide
You do not need to explicitly make the getAdvertisingToken() method call to retrieve the advertising tokens and pass them into Google GMA/IMA SDK manually. The UID2 GMA/IMA plugins manage this for you.
All you need to do is make sure that getAdvertisingToken() returns a non-null string object:
- Android
- iOS
UID2Manager.getInstance().getAdvertisingToken()
UID2Manager.shared.getAdvertisingToken()
If the token exists, the Google GMA/IMA plug-ins can retrieve it automatically via the UID2 GMA/IMA plugins.
Optional: UID2 Integration with Prebid Mobile SDK
The UID2 integration with Prebid Mobile SDK v2 requires version 1.6.0 of the UID2 SDK for Android, or version 1.7.0 of the UID2 SDK for iOS.
If you are using Prebid Mobile SDK v3, version 2.0.0 of the UID2 SDK for Android or iOS is required.
This section is for participants who want to integrate with UID2 and use the Prebid Mobile SDK for header bidding in Android and iOS applications.
The UID2 Prebid integration monitors the state of the UID2Identity. Whenever the state changes, the Prebid integration automatically updates Prebid’s external user IDs. This includes when an identity is refreshed, resulting in a new advertising token.
Prebid then sends the UID2 tokens into the RTB bidstream, along with other external user IDs that you might set.
This integration requires a Prebid Server setup.
To configure your UID2 Prebid for Mobile integration, follow these steps:
-
Set up Prebid's Mobile SDK, following the steps in Prebid SDK Integration for Android or Prebid SDK Integration for iOS.
-
Add the UID2 Mobile SDK to your app, following the steps in Add the UID2 Mobile SDK to Your Mobile App.
-
The UID2 Prebid integration is distributed as a separate module, so you must add it as a dependency in your project. Follow the installation instructions that apply to your integration, out of the following options:
- Gradle (Android)
- Maven (Android)
- CocoaPods (iOS)
- SPM (iOS)
Include the following in your Gradle configuration:
implementation("com.uid2:uid2-android-sdk-prebid:2.0.0")To install with Maven, add the SDK as a dependency in the
pom.xmlfile:<dependency>
<groupId>com.uid2</groupId>
<artifactId>uid2-android-sdk-prebid</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>Add the following entry in your
Podfile:pod 'UID2Prebid', '~> 2.0'In the XCode user interface, under Package Dependencies, add the following url and choose to add
UID2Prebidto your target.https://github.com/IABTechLab/uid2-ios-sdk.git -
After adding the dependency, you'll need to configure the integration. First initialize the
UID2Manager, and then Prebid, as shown in the following examples.- Android Kotlin
- Android Java
- iOS Swift
UID2Manager.init(context = this)
PrebidMobile.initializeSdk(this) { Log.i(TAG, "Prebid: $it") }
prebid = UID2Prebid(UID2Manager.getInstance()).apply {
initialize()
}UID2Manager.init(this);
PrebidMobile.initializeSdk(this, status -> Log.i(TAG, "Prebid: " + status));
prebid = new UID2Prebid(UID2Manager.getInstance());
prebid.initialize();Initialize an instance of UID2Prebid and hold a strong reference to it. UID2Prebid only observes the UID2Manager while the instance is retained.
self.prebid = UID2Prebid(manager: UID2Manager.shared) -
Configure a callback that's passed in during initialization.
The UID2 Prebid integration periodically updates Prebid by setting the relevant external IDs when a new identity is generated or an existing token is refreshed.
This process is destructive, which means that if your application uses external IDs from another source, you'll need to provide those to the UID2 Prebid integration so that all external IDs are retained while the UID2 token is updated.
This is done via the callback, which must be passed in during initialization, as shown in the following examples.
- Android Kotlin
- Android Java
- iOS Swift
prebid = UID2Prebid(
manager = UID2Manager.getInstance(),
externalUserIdFactory = ::getExternalIds,
).apply {
initialize()
}prebid = new UID2Prebid(UID2Manager.getInstance(), () -> getExternalIds());
prebid.initialize();self.prebid = UID2Prebid(manager: UID2Manager.shared, thirdPartyUserIDs: {
// return externalUserIDs
})
Error Response States
In certain conditions, the mobile SDK might return one of the following error response states:
The response states are the same for both Android and iOS.
Response State of Expired
A response state of Expired means that the UID2 token has expired but the refresh token has not expired, therefore the UID2 token can be refreshed.
Automatic refresh: If you have automatic refreshing enabled on the SDK (automaticRefreshEnabled property), which is the default setting, the SDK refreshes the token for you. However, there are some scenarios where you might observe this state.
For example, if the app is launched and the SDK is immediately queried, you might see a response state of Expired while, in the background, the SDK is in the process of refreshing the token and will quickly update with the new identity.
In this scenario, no action is needed. As soon as the SDK is initialized, it will refresh the token.
Manual refresh: If you've disabled automatic refreshing of the token, and get a response state of Expired, you can manually request the refresh by calling the refreshIdentity() method.
Response State of RefreshExpired
A response state of RefreshExpired means that the UID2 token and the refresh token have both expired, therefore the UID2 token cannot be refreshed.
An example of how this could occur is if a user does not run your app for a long time, and the SDK therefore doesn't get an opportunity to refresh the UID2 token before the refresh token expires.
In this scenario, you'd need to regenerate the identity.
Response State of Invalid
A response state of Invalid means that the identity, whether loaded off disk or requested via the API, did not include all the necessary tokens. This should never happen, but might occur in unexpected circumstances.
If the SDK detects this error, it clears any previous identity since it's considered unusable.
In this scenario, you'd need to regenerate the identity. Ideally, also report the issue to your UID2 contact.
Response State of NoIdentity
A response state of NoIdentity means that the SDK has been initialized, but doesn't yet have a current identity.
This happens the first time the SDK is used on a device, before any identity has been generated. In this scenario, you'd need to generate the identity.